BMI Calculator
Use our free BMI Calculator to check your weight status and take the first step toward a healthier lifestyle!
The Ultimate Guide to BMI Calculation:
The Basics of Your Body Mass Index
What is BMI (Body Mass Index)?
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a value used to determine whether an individual has a normal weight for their height. It is obtained by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in metres and is expressed as kg/m². BMI is a rough indicator of the level of body fat and can be used to determine the risk of various diseases in different weight categories.
How to Calculate Your BMI?
BMI is calculated using the following formulas:
Metric System (kg/m²)
Imperial System (lbs/in²)
For instance, if a person weighs 70kg and is 1.75 m tall then their BMI is:
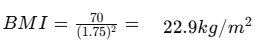
This is in the ‘normal’ weight category.
BMI Categories: What Does Your BMI Mean?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established categories of BMI as follows:
| Category |
BMI Range (kg/m²)
|
| Severe Thinness | <16 |
| Moderate Thinness | 16 – 17 |
| Mild Thinness | 17 – 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 25 |
| Overweight | 25 – 30 |
| Obese Class I | 30 – 35 |
| Obese Class II | 35 – 40 |
| Obese Class III | >40 |
BMI Understanding for Different Age Groups
BMI is more suitable for adults over the age of 20 while for children and teenagers it is rather different. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers BMI-for-age growth charts that classify children’s weight status by percentiles:
| Category |
Percentile Range
|
| Underweight | <5% |
| Healthy Weight | 5% – 85% |
| At Risk of Overweight | 85% – 95% |
| Overweight | >95% |
Since children are still growing, BMI is compared with others of the same age and gender but not set numerical values.
The Health Risks of an Abnormal BMI
The complications of being overweight or obese include the following:
-
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
- High blood pressure and cholesterol
- Type 2 diabetes
- Joint problems (osteoarthritis)
- Sleep apnea and breathing difficulties
- Certain cancers (colon, breast, kidney, etc.) are more likely to develop.
- Complications of Being Underweight:
- Not getting enough nutrients from foods, including vitamins, minerals, and protein
- Osteoporosis and weak bones
- Lowered immune system
- Difficulty getting pregnant and other complications during pregnancy
- Increased risk of complications during and after surgeries
Limitations of BMI: The Reasons Why It is Inaccurate
Although BMI is a valuable indicator, it has its limitations. The following are some key limitations;
Muscle Mass: Athletes and bodybuilders are likely to have high BMIs due to muscle and not fat.
Body Composition: The BMI does not consider fat mass, muscle mass, and bone mass.
Age and Gender Effects: Older people tend to have more fat than younger people with the same BMI, and women have more fat than men.
Ethnic Differences: Some ethnic groups may have different health risks at the same BMI.
For a more accurate assessment, other measures like body fat percentage, waist to hip ratio and the Ponderal Index should also be used.
What is BMI Prime?
BMI Prime is a modified version of the BMI index that compares the BMI value of a person to the upper limit of the ‘normal weight’ category (BMI 25 kg/m²): A BMI Prime less than 1 implies that a person is within the normal range, while values higher than 1 suggest overweight or obesity.
Ponderal Index: A Better Way to Measure Body Fatness?
The Ponderal Index (PI) is another method of evaluating body leanness and is especially useful for very tall or short people. Unlike BMI where height is squared, in PI it is cubed:
The use of PI is more appropriate for those who are not in the average height category.
How to Keep a Healthy BMI
1. Balanced Diet
-
- Consume whole foods, lean proteins, and unprocessed vegetables.
- Avoid foods that have been processed, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough water.
2. Regular Physical Activity
-
- Try to achieve at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise every week.
- Strengthening exercises should also be included to prevent loss of muscle mass.
- Increase daily activity by walking, taking the stairs, and reducing the time spent sitting.
3. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
-
- Get enough sleep (7-9 hours per night).
- Cope with stress through mindfulness, meditation, or any other hobby.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake.
Final Thoughts: Should You Rely Solely on BMI?
BMI is a useful indicator of potential weight-related health issues, but it should not be used as the sole measure of health. It is crucial to take into account other factors like body composition, fitness level, and general health. A healthcare professional can give a more accurate evaluation of the situation.